Before I hand over this guide to you and you start using VBA to create a pivot table, let me confess something. I learned to use VBA a decade ago.
The first time I wrote a macro code to create a pivot table, it was a failure. Since then, I have learned more from my bad coding than from the codes that work.
Today, I will show you a simple way to automate your pivot tables using a macro code.
Normally, when you insert a pivot table in a worksheet, it happens through a simple process, but that entire process is so quick that you never notice what happened.
In VBA, that entire process is the same, just executed using code. In this guide, I’ll show you each step and explain how to write code for it.
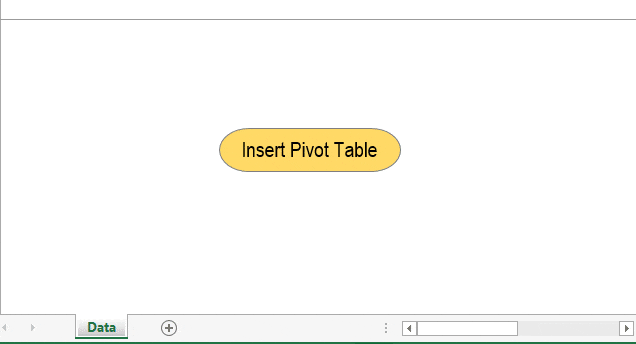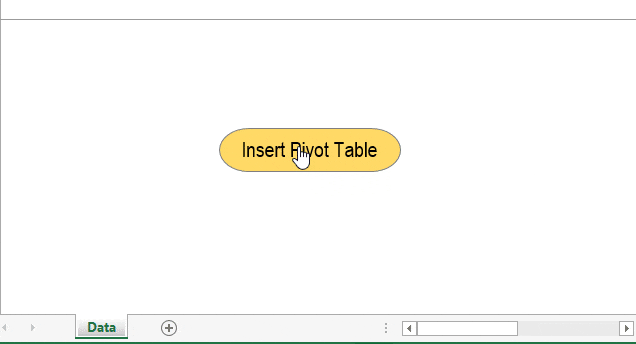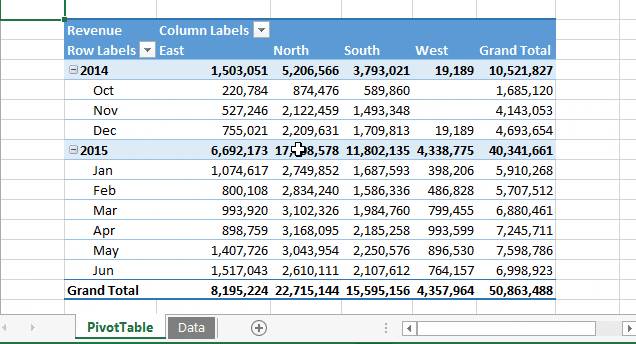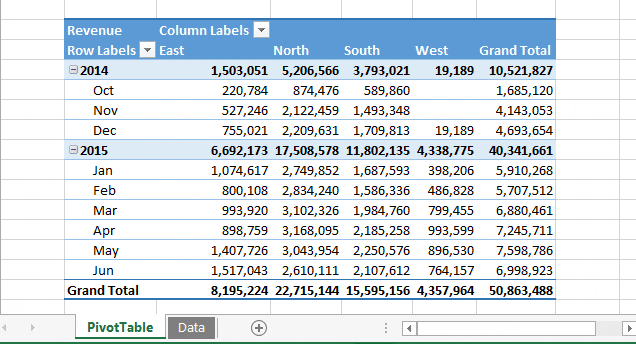
Just look at the example below, where you can run this macro code with a button, and it returns a new pivot table in a new worksheet in a flash.
Without any further ado, let’s get started writing our macro code to create a pivot table.
[FULL CODE] Use VBA to Create a Pivot Table in Excel – Macro to Copy-Paste
Sub InsertPivotTable()
'Macro By ExcelChamps.com
'Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As Long
'Insert a New Blank Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("PivotTable").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "PivotTable"
Set PSheet = Worksheets("PivotTable")
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Sales_Data")
'Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
'Define Pivot Cache
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _
SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange)
'Insert Pivot Table
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), TableName:="SalesPivotTable")
'Insert Row Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Region")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Salesperson")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 2
End With
'Insert Column Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Product")
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End With
'Insert Data Field
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = "#,##0"
.Name = "Revenue"
End With
'Format Pivot Table
PTable.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
PTable.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
End SubGet the Sample File (EC0010)
The Simple 8 Steps to Write a Macro Code in VBA to Create a Pivot Table in Excel
I have split the entire process into 8 simple steps for your convenience. After following these steps, you will be able to automate all your pivot tables.
1. Declare Variables
The first step is to declare the variables we need to use in our code to define different things.
'Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As LongHere’s what each line does:
- Dim PSheet As Worksheet: This line declares a Workbook object variable named PSheet, representing a worksheet where the pivot table will be created.
- Dim DSheet As Worksheet: This line declares another Workbook object variable named DSheet, which will represent the worksheet that contains the source data.
- Dim PCache As PivotCache: This line declares a PivotCache object variable named PCach, used to store the data for the pivot table.
- Dim PTable As PivotTable: This line declares a PivotTable object variable namedPTable`, which will represent the pivot table itself.
- Dim PRange As Range: This line declares a Range object variable named PRange, representing the data range the pivot table will analyze.
- Dim LastRow As Long: This line declares a Long variable named LastRow, which will store the row number of the last row in the data set.
- Dim LastCol As Long: This line declares another Long variable named LastCol, which will be used to store the column number of the last column in the data set.
2. Insert a New Worksheet
Before creating a pivot table, Excel inserts a blank sheet and then creates a new pivot table there.

And, the below code will do the same for you.
'Declare Variables
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("PivotTable").Delete
Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "PivotTable"
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Set PSheet = Worksheets("PivotTable")
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Data")- On Error Resume Next: This line prevents the code from stopping if it encounters an error. Instead, it ignores the error and moves to the next line of code.
- Application.DisplayAlerts = False: This line turns off alerts and warnings that Excel might show while running the code.
- Worksheets(“PivotTable”).Delete: This line deletes the worksheet named “PivotTable” if it exists already.
- Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet: This line adds a new sheet before the current active sheet.
- ActiveSheet.Name = “PivotTable”: This line renames the newly created sheet to “PivotTable”.
- Application.DisplayAlerts = True: This line turns the alerts back on after the operations are done.
- Set PSheet = Worksheets(“PivotTable”): This line creates a reference to the “PivotTable” worksheet and assigns this reference to the variable PSheet.
- Set DSheet = Worksheets(“Data”): This line creates a reference to the “Data” worksheet and assigns this reference to the variable DSheet.
After inserting a new worksheet, this code will set the value of the PSheet variable to the pivot table worksheet and DSheet to the source data worksheet.
Note – Make sure to change the name of the worksheets in the code to the names that you have in your data.
3. Define Data Range
Now, the next thing is to define the data range from the source worksheet. Here, you need to take care of one thing: you can’t specify a fixed source range.
You need a code that can identify the entire data from the source sheet. Below is the code:
'Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)- LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row: This line finds the last row of the first column (column 1) with data. Rows.Count gives the total number of rows in the worksheet, and End(xlUp) moves up from the bottom until it finds a cell with data.
- LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column: This line finds the last column of the first row (row 1) with data. Columns.Count gives the total number of columns in the worksheet, and End(xlToLeft) moves to the left from the far right of the worksheet until it finds a cell with data.
- Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol): This line sets a range that starts from the cell in the first row and first column (Cell 1, 1) and resizes it to include all cells until the last row with data and the last column with data. PRange now refers to the range of cells that contains data in the worksheet.
Note – You don’t need to change the data source every time while creating the pivot table.
4. Create a Pivot Cache
In Excel 2000 and above, before creating a pivot table, you need to create a pivot cache to define the data source.
Normally, when you create a pivot table, Excel automatically creates a pivot cache without asking you, but when you need to use VBA, you need to write code for this.
'Define Pivot Cache
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _
SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange)- TableName:=”SalesPivotTable”: This parameter in the
CreatePivotTablemethod sets the name of the pivot table being created. In this case, the pivot table will be named “SalesPivotTable”. - Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create: This line of code is initializing the creation of a cache for the pivot table. A pivot cache is a particular type of data structure that Excel uses to store a snapshot of the source data for a pivot table. The
ActiveWorkbookobject refers to the active workbook in the Excel application. - SourceType:=xlDatabase: This line in the
Createmethod specifies the type of data source used for the pivot table. ThexlDatabasevalue indicates that the source data is coming from a database, which in Excel could be a range of cells in a spreadsheet structured like a database. - SourceData:=PRange: This line in the Create method specifies the data used for the pivot table. In this case, the
PRangerefers to a named range in the workbook that contains the source data. - .CreatePivotTable: This method is called on the pivot cache object (
PCache) and creates the pivot table from the data stored in it. - TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2): This parameter in the CreatePivotTable method specifies where the upper-left cell of the pivot table will be added in the worksheet. The PSheet.Cells(2,2) value represents the cell in the second row and second column of the sheet referred to by PSheet.
5. Insert a Blank Pivot Table
After the pivot cache, the next step is to insert a blank pivot table.
Just remember when you create a pivot table, what happens, you always get a blank pivot first, and then you define all the values, columns, and rows.

This code will do the same:
'Insert Pivot Table
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), TableName:="SalesPivotTable")This code creates a blank pivot table and names it “SalesPivotTable”. You can change this name from the code itself.
6. Insert Row and Column Fields
After creating a blank pivot table, the next thing is to insert row and column fields, just like you do normally.
For each row and column field, you need to write a code.
Here we want to add years and months in the row field and zones in the column field.
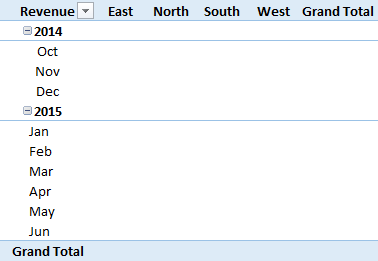
Here is the code:
'Insert Row Fields
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").PivotFields("Year")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").PivotFields("Month")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 2
End With
'Insert Column Fields
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").PivotFields("Zone")
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End WithIn this code, you have mentioned year and month as two fields. Now, if you look at the code, you’ll find that a position number is also there.
This position number defines the sequence of fields.
Whenever you need to add more than one field (Row or Column), specify their position.
You can change fields by editing their name from the code.
7. Insert Values
The main thing is to define the value field in your pivot table.
The code for defining values differs from defining rows and columns because we must define the formatting of numbers, positions, and functions here.
'Insert Data Field
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").PivotFields("Amount")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = "#,##0"
.Name = "Revenue "
End WithYou can add the amount as the value field with the above code. And this code will format values as a number with a (,) separator.
We use xlsum to sum values, but you can also use xlcount and other functions.
8. Format Pivot Table
You need to use a code to format your pivot table. There is a default formatting in a pivot table, but you can change that formatting.
With VBA, you can define formatting styles within the code.
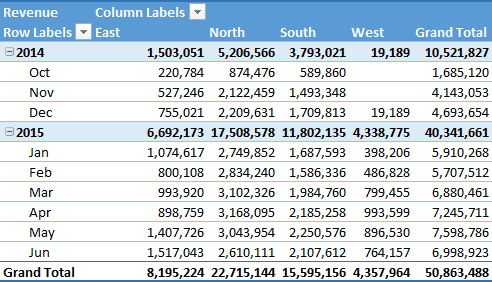
Code is:
'Format Pivot
TableActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"The above code will apply row strips and the “Pivot Style Medium 9” style, but you can also use another style from this link.
Finally, your code is ready to use.
[FULL CODE] VBA Code to Create Multiple Pivot Tables from the Same Data Source.
The code below creates eight pivot tables on a new worksheet from the same data source.
Sub Insert_Multiple_Pivot_Tables()
'Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As Long
Dim pvt As PivotTable
'Delete and Add Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("PivotTable").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "PivotTable"
Set PSheet = Worksheets("PivotTable")
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Sales_Data")
'Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
'Create Pivot Cache Once
'Create a Pivot Cache from the source data range only once
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _
SourceType:=xlDatabase, _
SourceData:=PRange)
'Pivot 1 – Region-Wise Total Sales
'Create Pivot Table for Region-Wise Total Sales
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("A1"), _
TableName:="Pivot1_RegionSales")
With PTable.PivotFields("Region")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot1_RegionSales"
End With
'Pivot 2 – Product-Wise Total Sales
'Create Pivot Table for Product-Wise Total Sales
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("A8"), _
TableName:="Pivot2_ProductSales")
With PTable.PivotFields("Product")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot2_ProductSales"
End With
'Pivot 3 – Payment Mode Wise Total Sales
'Create Pivot Table for Payment Mode-Wise Total Sales
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("D1"), _
TableName:="Pivot3_PaymentSales")
With PTable.PivotFields("Payment Mode")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot3_PaymentSales"
End With
'Pivot 4 – Delivery Status Wise Units Sold
'Create Pivot Table for Delivery Status-Wise Units Sold
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("D9"), _
TableName:="Pivot4_DeliveryUnits")
With PTable.PivotFields("Delivery Status")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Units Sold")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot4_DeliveryUnits"
End With
'Pivot 5 – Customer Type Wise Total Sales
'Create Pivot Table for Customer Type-Wise Total Sales
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("G1"), _
TableName:="Pivot5_CustomerSales")
With PTable.PivotFields("Customer Type")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot5_CustomerSales"
End With
'Pivot 6 – Order Priority Wise Units Sold
'Create Pivot Table for Order Priority-Wise Units Sold
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("A19"), _
TableName:="Pivot6_PriorityUnits")
With PTable.PivotFields("Order Priority")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Units Sold")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot6_PriorityUnits"
End With
'Pivot 7 – Warranty Wise Units Sold
'Create Pivot Table for Warranty-Wise Units Sold
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("D16"), _
TableName:="Pivot7_WarrantyUnits")
With PTable.PivotFields("Warranty")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Units Sold")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot7_WarrantyUnits"
End With
'Pivot 8 – Return Eligibility Wise Units Sold
'Create Pivot Table for Return Eligibility-Wise Units Sold
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("G8"), _
TableName:="Pivot8_ReturnUnits")
With PTable.PivotFields("Return Eligibility")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Units Sold")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot8_ReturnUnits"
End With
'Loop through each Pivot Table on the PivotTable worksheet to apply formatting
For Each pvt In PSheet.PivotTables
pvt.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
pvt.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
Next pvt
End Sub
Just like the code that we have used to create a single pivot table, this code inserts a new worksheet with the name Pivot Table and then creates 8 different pivot tables on that sheet.
Then it goes to the SalesData worksheet and defines the source data that it will use to create a pivot cache.
As you have the same data source, instead of creating a pivot cache with each pivot table, this code creates a single pivot cache and then use it for creating each of the pivot tables.
And then insert eight pivot tables one by one using a different location within the worksheet so that none of the pivot table overlaps the other.
[FULL CODE] Pivot Table on the Existing Worksheet
Sub Insert_Pivot_Tables_Existing_Sheet()
Dim wsName As String
Dim TargetSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long, LastCol As Long
Dim LastUsedRow As Long
Dim InsertCell As Range
'Ask user for the sheet name
wsName = InputBox( _
Prompt:="Enter sheet name to insert a pivot table.", _
Title:="Target Sheet")
'Check if sheet exists
On Error Resume Next
Set TargetSheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(wsName)
On Error GoTo 0
If TargetSheet Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Sheet '" & wsName & "' does not exist.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
'Set source data sheet
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Sales_Data")
'Define source data range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
'Check if the sheet has any content
Dim lastCell As Range
Set lastCell = TargetSheet.Cells.Find("*", SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If lastCell Is Nothing Then
'Sheet is blank, so insert at B2
Set InsertCell = TargetSheet.Range("B2")
Else
'Sheet has data, insert pivot 2 rows below the last used row
LastUsedRow = lastCell.Row
Set InsertCell = TargetSheet.Cells(LastUsedRow + 2, 2)
End If
'Create Pivot Cache
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange)
'Create the Pivot Table at the target cell with a unique name based on current time
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=InsertCell, _
TableName:="SalesPivot_" & Format(Now, "hhmmss"))
'Add Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Region")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Salesperson")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 2
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Product")
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = "#,##0"
.Name = "Revenue"
End With
'Apply style
With PTable
.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
End With
MsgBox "Pivot Table inserted in '" & wsName & _
"' sheet at cell " & InsertCell.Address, vbInformation
End SubAdding a Filter along with Creating a Pivot Table
Below are a simple lines of code that you can use while writing a code to create a pivot table that allows you to add a filter to the pivot table.
With PTable.PivotFields("Year")
.Orientation = xlPageField
.Position = 1
End WithHere is the complete code that can create a new pivot table and add a “Year” column as a filter for the pivot table.
Sub InsertPivotTable()
'Macro By ExcelChamps.com
'Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As Long
'Insert a New Blank Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("PivotTable").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "PivotTable"
Set PSheet = Worksheets("PivotTable")
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Sales_Data")
'Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
'Define Pivot Cache
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _
SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange)
'Insert Pivot Table
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), TableName:="SalesPivotTable")
'Insert Filter Field (Page Field)
With PTable.PivotFields("Location")
.Orientation = xlPageField
.Position = 1
End With
'Insert Row Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Region")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Salesperson")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 2
End With
'Insert Column Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Product")
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End With
'Insert Data Field
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = "#,##0"
.Name = "Revenue"
End With
'Format Pivot Table
PTable.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
PTable.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
End Sub[SAMPLE FILES] (EC0010)
In the end,
By using this code, we can automate your pivot tables.
And the best part is this is a one-time setup; after that, we just need a click to create a pivot table, and you can save a ton of time.
Now tell me one thing.
Have you ever used a VBA code to create a pivot table?
Please share your views with me in the comment box; I’d love to share them with you and share this tip with your friends.
VBA is one of the Advanced Excel Skills, and if you are getting started with VBA, make sure to check out the Useful Macro Examples and VBA Codes.
This was very easy to follow, it worked perfectly! THANK YOU!
This worked… Sort of.
I could set the Row and Column of the PT, but not the Data Field when I changed it from Sum to Count. Ended up recording a macro to set the data field and then pasted the code into the module and it now works. See below for your code (with count instead of sum), and the changes I made.
‘Insert Data Field
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“409PivotTable”)
‘THIS WAS THE FROM THE ORIGINAL EX. CODE THAT DIDN’T SEEM TO WORK
‘.PivotFields (“total_rec”)
‘.Orientation = xlDataField
‘.Function = xlCount
‘.Caption = “Special Name”
‘.NumberFormat = “#,##0”
‘.Name = “409PivotTable”
‘THIS IS A COPY/PASTE FROM RECORDING A MACRO TO ADD THE VALUES FIELD
ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“409PivotTable”).AddDataField ActiveSheet.PivotTables( _
“409PivotTable”).PivotFields(“assignedownergroup”), “Count of assignedownergroup”, _
xlCount
End With
Dear excelchamps,
I have tried above PivotTable coding, i have below mention 2 queries,
1. it is showing object variable or with block variable not set.
2. I wanted to taken pivot from second row
Please help me to find my resolution.
Thanks in advance…
This is an excellent way of explaining. Great job!
Puneet:
Please allow me to explain what I am trying to do. Part one of my Macro pulls data into an Excel sheet. Part two then takes the data and parses it into a usable form. For part three, I’d like to have VBA automatically create pivot tables. However, I want to incorporate “Distinct Count” into dome of the pivots. From using the macro recorder, I see that ADD2 is used to make a data connection. I have tried to develop a way to have VBA automatically make the connection, but my attempts are not successful. The Connection String seems to be consistent. Thus, this could be easily written into VBA. I have tried to use Range to deal with the objects in ADD2. In other words, I have the appropriate wording in cells and point the VBA to those cells. Yet, I am still not able to get this to work. If need be, I can send you my code. Thanks!
Puneet: This was excellent information. Thank you! The one thing I seem to be struggling with is how to have VBA generate a Pivot Table that incorporates a Data Model. I have been unsuccessful thus far in writing such a macro. Any thoughts on how to do this?
need more words from you on this.
Great post.
one thing i’m struggling with is to convert the pivot into classic view.
please help
i tried adding this part of the script at the end but no change
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“Comm”)
.InGridDropZones = True
.RowAxisLayout xlTabularRow
End With
Your step by step tutorial is great, defining a dynamic range for my dataset was a challenge and you simplified it. Thank you, all the best to you.
Great post! Thanks a lot.
Hi,
Thanks for the code.
1. Could you please advise how to create a filter on a column so that only selected data will appear in the pivot table?
2. Could you please show an example of creating a new column based on calculation from the existing table?
Thanks again
Thanks, I managed to create my 1st pivot table using your code. If I want to use the same data source to create 2nd pivot table in different sheet (eg. sheet2), how do I go about it?
this is awesome stuff. Thanks!
Je suis très ravi de trouver les solutions à mes difficultés concernant la création d’un Tableau croisé Dynamique par VBA
Get error 5 when I try to create a pivot table. I have done this in the past but in Office 2016 I can’t get it to work.
Terry, try with the sample file once.
Hi Puneet,
Thanks a lot for this free tutorial on Pivot table by VBA. I am a 65 years old mathematics teacher, who also handles data analysis. Although built in pivot table serves my purpose, I have been curious to create one using VBA.
Thanks a lot once again.
Ashokan
Singapore
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create _
(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange). _
CreatePivotTable(TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(20, 2), _
TableName:=”TeamQualityMetrics”)
Dear Sir,
On this I am getting a compile error, Method or data member not found.
Can you pls help
Regards
Manoj
I have delete that part of the code and add it like this and it is working for me:
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow1, LastCol)
ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:= _
PRange, Version:=6).CreatePivotTable TableDestination:= _
“PivotTable!R1C1″, TableName:=”SalesPivotTable”, DefaultVersion:=6
Sheets(“PivotTable”).Select
Cells(1, 1).Select
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“SalesPivotTable”)
.ColumnGrand = True
.HasAutoFormat = True
.DisplayErrorString = False
.DisplayNullString = True
.EnableDrilldown = True
.ErrorString = “”
.MergeLabels = False
.NullString = “”
.PageFieldOrder = 2
.PageFieldWrapCount = 0
.PreserveFormatting = True
.RowGrand = True
.SaveData = True
.PrintTitles = False
.RepeatItemsOnEachPrintedPage = True
.TotalsAnnotation = False
.CompactRowIndent = 1
.InGridDropZones = False
.DisplayFieldCaptions = True
.DisplayMemberPropertyTooltips = False
.DisplayContextTooltips = True
.ShowDrillIndicators = True
.PrintDrillIndicators = False
.AllowMultipleFilters = False
.SortUsingCustomLists = True
.FieldListSortAscending = False
.ShowValuesRow = False
.CalculatedMembersInFilters = False
.RowAxisLayout xlCompactRow
End With
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“SalesPivotTable”).PivotCache
.RefreshOnFileOpen = False
.MissingItemsLimit = xlMissingItemsDefault
End With
ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“SalesPivotTable”).RepeatAllLabels xlRepeatLabels
‘Insert Row Fields
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“SalesPivotTable”).PivotFields(“Local Legal Entity Code”)
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
Please explain 6 or multiple pivot table creation on a single worksheet
Hello. Thank you for the great tutorial.
Can you please explain how I can add the coding to this VBA Project to select the check box “Add this data the the Data Model” located at the bottom of the in the Create Pivot Table Screen?
What is the code to change to show to subtotals, collapse buttons + – and to view in Tabular?
Thanks,
Victor
Hi,
I used your code, and it works great! But my pivot does not need a column field, so I removed the code to add the column field (i.e. my column would just show sum of sales) but now it doesn’t show any values. It just gives me the rows