Before I hand over this guide to you and you start using VBA to create a pivot table, let me confess something. I learned to use VBA a decade ago.
The first time I wrote a macro code to create a pivot table, it was a failure. Since then, I have learned more from my bad coding than from the codes that work.
Today, I will show you a simple way to automate your pivot tables using a macro code.
Normally, when you insert a pivot table in a worksheet, it happens through a simple process, but that entire process is so quick that you never notice what happened.
In VBA, that entire process is the same, just executed using code. In this guide, I’ll show you each step and explain how to write code for it.
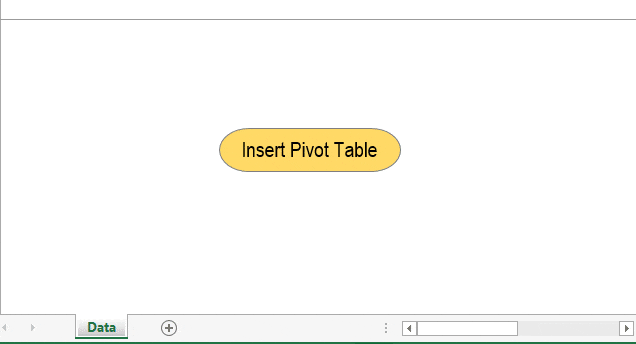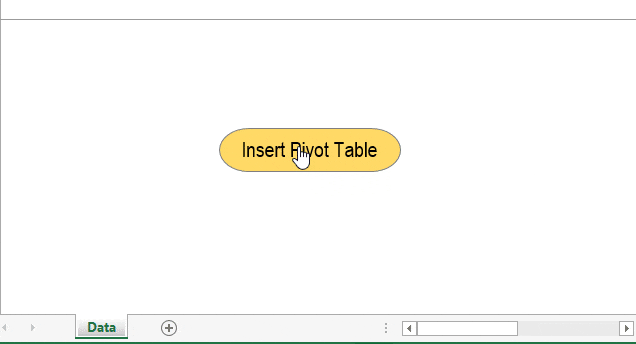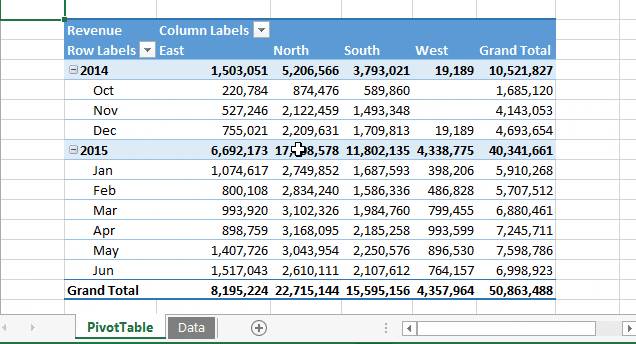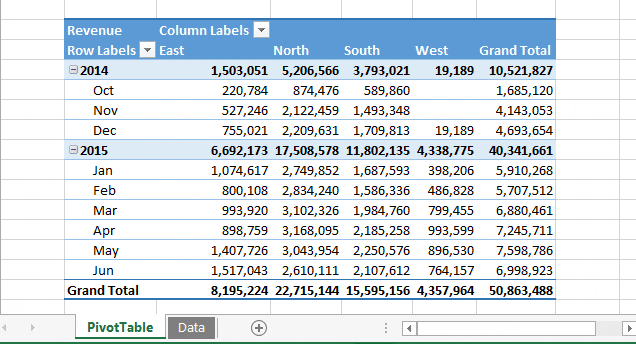
Just look at the example below, where you can run this macro code with a button, and it returns a new pivot table in a new worksheet in a flash.
Without any further ado, let’s get started writing our macro code to create a pivot table.
[FULL CODE] Use VBA to Create a Pivot Table in Excel – Macro to Copy-Paste
Sub InsertPivotTable()
'Macro By ExcelChamps.com
'Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As Long
'Insert a New Blank Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("PivotTable").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "PivotTable"
Set PSheet = Worksheets("PivotTable")
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Sales_Data")
'Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
'Define Pivot Cache
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _
SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange)
'Insert Pivot Table
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), TableName:="SalesPivotTable")
'Insert Row Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Region")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Salesperson")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 2
End With
'Insert Column Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Product")
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End With
'Insert Data Field
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = "#,##0"
.Name = "Revenue"
End With
'Format Pivot Table
PTable.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
PTable.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
End SubGet the Sample File (EC0010)
The Simple 8 Steps to Write a Macro Code in VBA to Create a Pivot Table in Excel
I have split the entire process into 8 simple steps for your convenience. After following these steps, you will be able to automate all your pivot tables.
1. Declare Variables
The first step is to declare the variables we need to use in our code to define different things.
'Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As LongHere’s what each line does:
- Dim PSheet As Worksheet: This line declares a Workbook object variable named PSheet, representing a worksheet where the pivot table will be created.
- Dim DSheet As Worksheet: This line declares another Workbook object variable named DSheet, which will represent the worksheet that contains the source data.
- Dim PCache As PivotCache: This line declares a PivotCache object variable named PCach, used to store the data for the pivot table.
- Dim PTable As PivotTable: This line declares a PivotTable object variable namedPTable`, which will represent the pivot table itself.
- Dim PRange As Range: This line declares a Range object variable named PRange, representing the data range the pivot table will analyze.
- Dim LastRow As Long: This line declares a Long variable named LastRow, which will store the row number of the last row in the data set.
- Dim LastCol As Long: This line declares another Long variable named LastCol, which will be used to store the column number of the last column in the data set.
2. Insert a New Worksheet
Before creating a pivot table, Excel inserts a blank sheet and then creates a new pivot table there.

And, the below code will do the same for you.
'Declare Variables
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("PivotTable").Delete
Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "PivotTable"
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Set PSheet = Worksheets("PivotTable")
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Data")- On Error Resume Next: This line prevents the code from stopping if it encounters an error. Instead, it ignores the error and moves to the next line of code.
- Application.DisplayAlerts = False: This line turns off alerts and warnings that Excel might show while running the code.
- Worksheets(“PivotTable”).Delete: This line deletes the worksheet named “PivotTable” if it exists already.
- Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet: This line adds a new sheet before the current active sheet.
- ActiveSheet.Name = “PivotTable”: This line renames the newly created sheet to “PivotTable”.
- Application.DisplayAlerts = True: This line turns the alerts back on after the operations are done.
- Set PSheet = Worksheets(“PivotTable”): This line creates a reference to the “PivotTable” worksheet and assigns this reference to the variable PSheet.
- Set DSheet = Worksheets(“Data”): This line creates a reference to the “Data” worksheet and assigns this reference to the variable DSheet.
After inserting a new worksheet, this code will set the value of the PSheet variable to the pivot table worksheet and DSheet to the source data worksheet.
Note – Make sure to change the name of the worksheets in the code to the names that you have in your data.
3. Define Data Range
Now, the next thing is to define the data range from the source worksheet. Here, you need to take care of one thing: you can’t specify a fixed source range.
You need a code that can identify the entire data from the source sheet. Below is the code:
'Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)- LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row: This line finds the last row of the first column (column 1) with data. Rows.Count gives the total number of rows in the worksheet, and End(xlUp) moves up from the bottom until it finds a cell with data.
- LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column: This line finds the last column of the first row (row 1) with data. Columns.Count gives the total number of columns in the worksheet, and End(xlToLeft) moves to the left from the far right of the worksheet until it finds a cell with data.
- Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol): This line sets a range that starts from the cell in the first row and first column (Cell 1, 1) and resizes it to include all cells until the last row with data and the last column with data. PRange now refers to the range of cells that contains data in the worksheet.
Note – You don’t need to change the data source every time while creating the pivot table.
4. Create a Pivot Cache
In Excel 2000 and above, before creating a pivot table, you need to create a pivot cache to define the data source.
Normally, when you create a pivot table, Excel automatically creates a pivot cache without asking you, but when you need to use VBA, you need to write code for this.
'Define Pivot Cache
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _
SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange)- TableName:=”SalesPivotTable”: This parameter in the
CreatePivotTablemethod sets the name of the pivot table being created. In this case, the pivot table will be named “SalesPivotTable”. - Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create: This line of code is initializing the creation of a cache for the pivot table. A pivot cache is a particular type of data structure that Excel uses to store a snapshot of the source data for a pivot table. The
ActiveWorkbookobject refers to the active workbook in the Excel application. - SourceType:=xlDatabase: This line in the
Createmethod specifies the type of data source used for the pivot table. ThexlDatabasevalue indicates that the source data is coming from a database, which in Excel could be a range of cells in a spreadsheet structured like a database. - SourceData:=PRange: This line in the Create method specifies the data used for the pivot table. In this case, the
PRangerefers to a named range in the workbook that contains the source data. - .CreatePivotTable: This method is called on the pivot cache object (
PCache) and creates the pivot table from the data stored in it. - TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2): This parameter in the CreatePivotTable method specifies where the upper-left cell of the pivot table will be added in the worksheet. The PSheet.Cells(2,2) value represents the cell in the second row and second column of the sheet referred to by PSheet.
5. Insert a Blank Pivot Table
After the pivot cache, the next step is to insert a blank pivot table.
Just remember when you create a pivot table, what happens, you always get a blank pivot first, and then you define all the values, columns, and rows.

This code will do the same:
'Insert Pivot Table
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), TableName:="SalesPivotTable")This code creates a blank pivot table and names it “SalesPivotTable”. You can change this name from the code itself.
6. Insert Row and Column Fields
After creating a blank pivot table, the next thing is to insert row and column fields, just like you do normally.
For each row and column field, you need to write a code.
Here we want to add years and months in the row field and zones in the column field.
Here is the code:
'Insert Row Fields
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").PivotFields("Year")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").PivotFields("Month")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 2
End With
'Insert Column Fields
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").PivotFields("Zone")
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End WithIn this code, you have mentioned year and month as two fields. Now, if you look at the code, you’ll find that a position number is also there.
This position number defines the sequence of fields.
Whenever you need to add more than one field (Row or Column), specify their position.
You can change fields by editing their name from the code.
7. Insert Values
The main thing is to define the value field in your pivot table.
The code for defining values differs from defining rows and columns because we must define the formatting of numbers, positions, and functions here.
'Insert Data Field
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").PivotFields("Amount")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = "#,##0"
.Name = "Revenue "
End WithYou can add the amount as the value field with the above code. And this code will format values as a number with a (,) separator.
We use xlsum to sum values, but you can also use xlcount and other functions.
8. Format Pivot Table
You need to use a code to format your pivot table. There is a default formatting in a pivot table, but you can change that formatting.
With VBA, you can define formatting styles within the code.
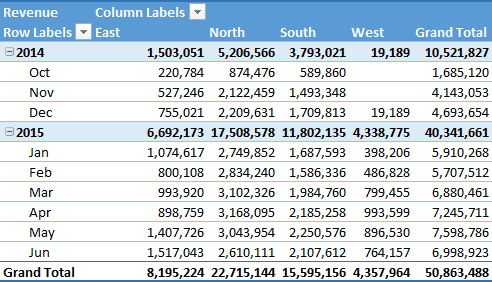
Code is:
'Format Pivot
TableActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
ActiveSheet.PivotTables("SalesPivotTable").TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"The above code will apply row strips and the “Pivot Style Medium 9” style, but you can also use another style from this link.
Finally, your code is ready to use.
[FULL CODE] VBA Code to Create Multiple Pivot Tables from the Same Data Source.
The code below creates eight pivot tables on a new worksheet from the same data source.
Sub Insert_Multiple_Pivot_Tables()
'Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As Long
Dim pvt As PivotTable
'Delete and Add Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("PivotTable").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "PivotTable"
Set PSheet = Worksheets("PivotTable")
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Sales_Data")
'Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
'Create Pivot Cache Once
'Create a Pivot Cache from the source data range only once
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _
SourceType:=xlDatabase, _
SourceData:=PRange)
'Pivot 1 – Region-Wise Total Sales
'Create Pivot Table for Region-Wise Total Sales
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("A1"), _
TableName:="Pivot1_RegionSales")
With PTable.PivotFields("Region")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot1_RegionSales"
End With
'Pivot 2 – Product-Wise Total Sales
'Create Pivot Table for Product-Wise Total Sales
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("A8"), _
TableName:="Pivot2_ProductSales")
With PTable.PivotFields("Product")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot2_ProductSales"
End With
'Pivot 3 – Payment Mode Wise Total Sales
'Create Pivot Table for Payment Mode-Wise Total Sales
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("D1"), _
TableName:="Pivot3_PaymentSales")
With PTable.PivotFields("Payment Mode")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot3_PaymentSales"
End With
'Pivot 4 – Delivery Status Wise Units Sold
'Create Pivot Table for Delivery Status-Wise Units Sold
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("D9"), _
TableName:="Pivot4_DeliveryUnits")
With PTable.PivotFields("Delivery Status")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Units Sold")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot4_DeliveryUnits"
End With
'Pivot 5 – Customer Type Wise Total Sales
'Create Pivot Table for Customer Type-Wise Total Sales
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("G1"), _
TableName:="Pivot5_CustomerSales")
With PTable.PivotFields("Customer Type")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot5_CustomerSales"
End With
'Pivot 6 – Order Priority Wise Units Sold
'Create Pivot Table for Order Priority-Wise Units Sold
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("A19"), _
TableName:="Pivot6_PriorityUnits")
With PTable.PivotFields("Order Priority")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Units Sold")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot6_PriorityUnits"
End With
'Pivot 7 – Warranty Wise Units Sold
'Create Pivot Table for Warranty-Wise Units Sold
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("D16"), _
TableName:="Pivot7_WarrantyUnits")
With PTable.PivotFields("Warranty")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Units Sold")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot7_WarrantyUnits"
End With
'Pivot 8 – Return Eligibility Wise Units Sold
'Create Pivot Table for Return Eligibility-Wise Units Sold
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Range("G8"), _
TableName:="Pivot8_ReturnUnits")
With PTable.PivotFields("Return Eligibility")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Units Sold")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.Name = "Pivot8_ReturnUnits"
End With
'Loop through each Pivot Table on the PivotTable worksheet to apply formatting
For Each pvt In PSheet.PivotTables
pvt.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
pvt.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
Next pvt
End Sub
Just like the code that we have used to create a single pivot table, this code inserts a new worksheet with the name Pivot Table and then creates 8 different pivot tables on that sheet.
Then it goes to the SalesData worksheet and defines the source data that it will use to create a pivot cache.
As you have the same data source, instead of creating a pivot cache with each pivot table, this code creates a single pivot cache and then use it for creating each of the pivot tables.
And then insert eight pivot tables one by one using a different location within the worksheet so that none of the pivot table overlaps the other.
[FULL CODE] Pivot Table on the Existing Worksheet
Sub Insert_Pivot_Tables_Existing_Sheet()
Dim wsName As String
Dim TargetSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long, LastCol As Long
Dim LastUsedRow As Long
Dim InsertCell As Range
'Ask user for the sheet name
wsName = InputBox( _
Prompt:="Enter sheet name to insert a pivot table.", _
Title:="Target Sheet")
'Check if sheet exists
On Error Resume Next
Set TargetSheet = ThisWorkbook.Worksheets(wsName)
On Error GoTo 0
If TargetSheet Is Nothing Then
MsgBox "Sheet '" & wsName & "' does not exist.", vbExclamation
Exit Sub
End If
'Set source data sheet
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Sales_Data")
'Define source data range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
'Check if the sheet has any content
Dim lastCell As Range
Set lastCell = TargetSheet.Cells.Find("*", SearchOrder:=xlByRows, SearchDirection:=xlPrevious)
If lastCell Is Nothing Then
'Sheet is blank, so insert at B2
Set InsertCell = TargetSheet.Range("B2")
Else
'Sheet has data, insert pivot 2 rows below the last used row
LastUsedRow = lastCell.Row
Set InsertCell = TargetSheet.Cells(LastUsedRow + 2, 2)
End If
'Create Pivot Cache
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange)
'Create the Pivot Table at the target cell with a unique name based on current time
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=InsertCell, _
TableName:="SalesPivot_" & Format(Now, "hhmmss"))
'Add Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Region")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Salesperson")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 2
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Product")
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = "#,##0"
.Name = "Revenue"
End With
'Apply style
With PTable
.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
End With
MsgBox "Pivot Table inserted in '" & wsName & _
"' sheet at cell " & InsertCell.Address, vbInformation
End SubAdding a Filter along with Creating a Pivot Table
Below are a simple lines of code that you can use while writing a code to create a pivot table that allows you to add a filter to the pivot table.
With PTable.PivotFields("Year")
.Orientation = xlPageField
.Position = 1
End WithHere is the complete code that can create a new pivot table and add a “Year” column as a filter for the pivot table.
Sub InsertPivotTable()
'Macro By ExcelChamps.com
'Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As Long
'Insert a New Blank Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
Worksheets("PivotTable").Delete
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
On Error GoTo 0
Sheets.Add Before:=ActiveSheet
ActiveSheet.Name = "PivotTable"
Set PSheet = Worksheets("PivotTable")
Set DSheet = Worksheets("Sales_Data")
'Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
'Define Pivot Cache
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create( _
SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange)
'Insert Pivot Table
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable( _
TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), TableName:="SalesPivotTable")
'Insert Filter Field (Page Field)
With PTable.PivotFields("Location")
.Orientation = xlPageField
.Position = 1
End With
'Insert Row Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Region")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
With PTable.PivotFields("Salesperson")
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 2
End With
'Insert Column Fields
With PTable.PivotFields("Product")
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End With
'Insert Data Field
With PTable.PivotFields("Total Sales")
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = "#,##0"
.Name = "Revenue"
End With
'Format Pivot Table
PTable.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
PTable.TableStyle2 = "PivotStyleMedium9"
End Sub[SAMPLE FILES] (EC0010)
In the end,
By using this code, we can automate your pivot tables.
And the best part is this is a one-time setup; after that, we just need a click to create a pivot table, and you can save a ton of time.
Now tell me one thing.
Have you ever used a VBA code to create a pivot table?
Please share your views with me in the comment box; I’d love to share them with you and share this tip with your friends.
VBA is one of the Advanced Excel Skills, and if you are getting started with VBA, make sure to check out the Useful Macro Examples and VBA Codes.
I am using office 365. Your code is note creating -data field. Even I tried with our example. can u correct for office 365 if an different
‘Insert Data Field
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“SalesPivotTable”)
.PivotFields (“Amount”)
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = “#,##0”
.Name = “Revenue ”
End With’Insert Data Field
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“SalesPivotTable”)
.PivotFields (“Amount”)
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Function = xlSum
.NumberFormat = “#,##0”
.Name = “Revenue ”
End With
Hi Piotr, i also had the same error. Guess you found the solution by yourself, but maybe for all other guys who come across.
The return value is a Pivottable not a Pivotcache. Change it to:
Set PTable = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create _
(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange). _
CreatePivotTable(TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), _
TableName:=”SalesPivotTable”)
This is not working still in Excel 2016. It says Run time error type mismatch. Can you please help?
Hi Dinesh,
Just wondering if you have found solution? I got the same error and cannot figure out how to solve it.
Kind regards,
Roy
Hi,
Can we play with Filter Option one by one in Pivot Table,
For example,
Step1: get the data corresponding the seet1.range A2
Step2: get the data corresponding to the sheet1.range A3
likewise.
Pl. help.
Hello
Using Excel 2010. I took this code from one of your examples and modified it to add in page fields
I have these two pieces of code below that put 2 fields into the page area of a pivot table.
I want to choose 2 out of 40 items in OrderID
I want to choose 1 out of 20 items in CustomerID
Is this possible without having to write true vs false code for each item in VBA?
Any alternative code greatly appreciated.
‘Insert Page Fields
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“SalesPivotTable”).PivotFields(“OrderID”)
.Orientation = xlPageField
.Position = 1
End With
With ActiveSheet.PivotTables(“SalesPivotTable”).PivotFields(“CustomerID”)
.Orientation = xlPageField
.Position = 2
End With
It works! Thank you so much!
You’re Welcome 🙂
Hello,
Please help in resolve the error.
ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:= _
“Sheet2!R1C1:R479C6”, Version:=6).CreatePivotTable TableDestination:= _
“Sheet3!R3C1″, TableName:=”PivotTable2”, DefaultVersion:=6
Hi the code works well thank you. I would like to add one more thing to it but can’t seem to figure it out. I want it to filter as per your example, 2014 only. How do I make it just show 2014 in my pivot? Don’t know if you can help but appreciate your post either way.
doesn’t seem to add Amount field to pivot table
Hi. The macro doesn’t work in excel 2010. When i step into (F8) the code to line ( I comment ‘ on error resume next ):
Set PCache = ActiveWorkbook.PivotCaches.Create _
(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange). _
CreatePivotTable(TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), _
TableName:=”SalesPivotTable”)
i have:
Run-time error 13 type mismatch.
Can you please help me?
Hi Punnett, this is brilliant, thank you. it wasnt working for me originally as i couldnt just copy and paste my data into a new worksheet – i had to make sure the data was set as a table.
Is there anyway to build the pivot table so that “Dsheet” doesnt have to be a table – just copied and pasted data with the first row to be used as the headers?
Thanks for posting this Puneet, this is exactly what i needed
Is there any way of amending the code so that it will work any worksheet and not just worksheets that are named “Data”?
You just need to change worksheet name in the code.
This is great! Thank you, Puneet!
I’m following up on Matt’s question. Is there any way to amend the code so I can run the macro regardless of the title on the worksheet without having to change the name in the code each time? I work with many data sets on a daily basis. Wondering if this is possible.
Puneet,
I am having trouble setting this up; very similar, yet a bit different. I will have the button on “Paste Data” sheet and it will be pulling the data to create the pivot from “Formatted” sheet.
Also, there is an additional column header. The setup of the pivot table should be as follows:
Filter – Order Type
Columns – Sum Values
Rows – 1. Salesman Name
2. G/L Cat
Values – 1. Sum of Extended Price
2. Sum of Commission Cost
I can email you the code if you’d like. Please advise.
Thanks!
This is Yaakov calling. Thank you very much for your kindness. Very inspiring and interesting site; I learn a lot from it. Keep on with the good work!
By the way trying your code worked just fine except for the ampunt field which did not show up automatically but i had to check it mannually. Reason?
Bye
Hi puneet,
Its awesome! Can i get this to my email!
This code does not work in Excel 2016
how to remove desirable variable from pivot table with vba
Hi Puneet,
Thanks for the awesome code. I completely believe it is useful for many. But I am getting error on running this code. I cant find the mistake I did while changing the code to match my sheet. Please help me to find the problem. The output for is a Pivot with Row and Column Fields with no Datafield. Below is my code:
Sub Total_Tickets_Created()
‘Declare Variables
Dim PSheet As Worksheet
Dim DSheet As Worksheet
Dim PCache As PivotCache
Dim PTable As PivotTable
Dim PRange As Range
Dim LastRow As Long
Dim LastCol As Long
Dim twb As Workbook
Set twb = ThisWorkbook
‘Insert a New Blank Worksheet
On Error Resume Next
Application.DisplayAlerts = False
twb.Worksheets(“Total Tickets Created”).Delete
Sheets.Add After:=Sheets(2)
ActiveSheet.Name = “Total Tickets Created”
Application.DisplayAlerts = True
Set PSheet = Worksheets(“Total Tickets Created”)
Set DSheet = Worksheets(“Case Advanced Find View”)
‘Define Data Range
LastRow = DSheet.Cells(Rows.Count, 1).End(xlUp).Row
LastCol = DSheet.Cells(1, Columns.Count).End(xlToLeft).Column
Set PRange = DSheet.Cells(1, 1).Resize(LastRow, LastCol)
‘Define Pivot Cache
Set PCache = twb.PivotCaches.Create _
(SourceType:=xlDatabase, SourceData:=PRange). _
CreatePivotTable(TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(2, 2), _
TableName:=”Total Tickets”)
‘Insert Blank Pivot Table
Set PTable = PCache.CreatePivotTable _
(TableDestination:=PSheet.Cells(1, 1), TableName:=”Total Tickets”)
‘Insert Row Fields
With Sheets(“Total Tickets Created”).PivotTables(“Total Tickets”).PivotFields(“Priority”)
.Orientation = xlRowField
.Position = 1
End With
‘Insert Column Fields
With Sheets(“Total Tickets Created”).PivotTables(“Total Tickets”).PivotFields(“Created Month”)
.Orientation = xlColumnField
.Position = 1
End With
‘Insert Data Field
With Sheets(“Total Tickets Created”).PivotTables(“Total Tickets”)
.PivotFields (“Case Number”)
.Orientation = xlDataField
.Position = 1
.Function = xlCount
.NumberFormat = “#,##0”
.Name = “Total Tickets”
.ShowTableStyleRowStripes = True
.TableStyle2 = “PivotStyleMedium9”
End With
End Sub
Thank you so much for this. Saved me a huge amount of time.
This is amazingly useful! I have been able to use it for my own work and it’s great. However, I do want to be able to nominate certain columns to go in the “Value” box of the pivot table (I need to count some cells). Whenever I try to do a “Count”, it seems to override the “insert row fields” function, so all I get is a count of the whole dataset, rather than a specific row. Any thoughts on how to get around this?
Many thanks, you da bomb
This article was so helpful! I was able to adapt the names to pull a table for my data without an issue. Now my only question is, how can I get it to pull a second pivot table from the same data on to the same worksheet?
Like, you want to create a new pivot table from the same source data and which need to have different fields? Correct me, if I’m wrong.