In Excel, there are multiple string (text) functions that can help you to deal with textual data. These functions can help you to change a text, change the case, find a string, count the length of the string, etc. In this post, we have covered top text functions. (Sample Files)
1. LEN Function
LEN function returns the count of characters in the value. In simple words, with the LEN function, you can count how many characters are there in value. You can refer to a cell or insert the value in the function directly.
Syntax
LEN(text)
Arguments
- text: A string for which you want to count the characters.
Example
In the below example, we have used the LEN to count letters in a cell. “Hello, World” has 10 characters with a space between and we have got 11 in the result.
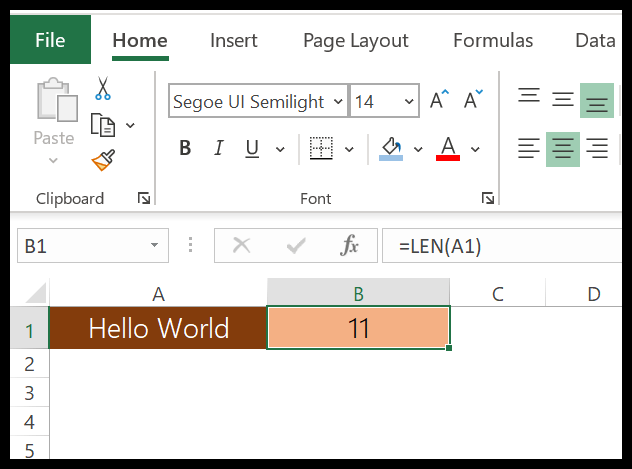
In the below example, “22-Jan-2016” has 11 characters, but LEN returns 5.
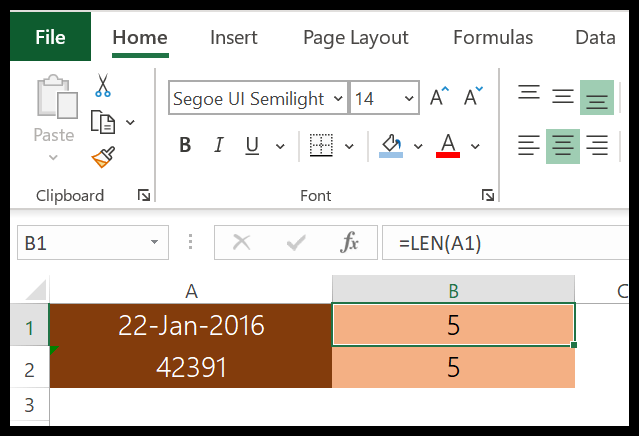
The reason behind it is that the LEN function counts the characters in the value of a cell and is not concerned with formatting.
Related: How to COUNT Words in Excel
2. FIND Function
FIND function returns a number which is the starting position of a substring in a string. In simple words, by using the find function you can find (case sensitive) a string’s starting position from another string.
Syntax
FIND(find_text,within_text,[start_num])
Arguments
- find_text: The text which you want to find from another text.
- within_text: The text from which you want to locate the text.
- [start_num]: The number represents the starting position of the search.
Example
In the below example, we have used the FIND to locate the “:” and then with the help of MID and LEN, we have extracted the name from the cell.
3. SEARCH Function
SEARCH function returns a number which is the starting position of a substring in a string. In simple words, with the SEARCH function, you can search (non-case sensitive) for a text string’s starting position from another string.
Syntax
SEARCH(find_text,within_text,[start_num])
Arguments
- find_text: A text which you want to find from another text.
- within_text: A text from which you want to locate the text. You can refer to a cell, or you can input a text in your function.
Example
In the below example, we are searching for the alphabet “P” and we have specified start_num as 1 to start our search. Our formula returns 1 as the position of the text.
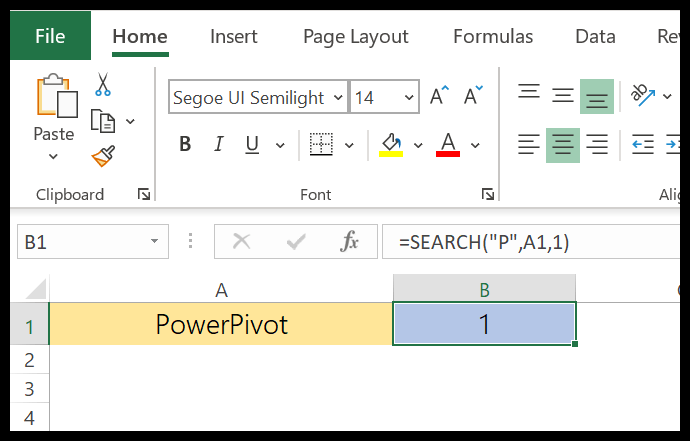
But, if you look at the word, we also have a “P” in the 6th position. That means the SEARCH function can only return the position of the first occurrence of a text, or if you specify the start position accordingly.
4. LEFT Function
LEFT Functions return sequential characters from a string starting from the left side (starting). In simple words, with the LEFT function, you can extract characters from a string from its left side.
Syntax
LEFT(text,num_chars)
Arguments
- text: A text or number from which you want to extract characters.
- [num_char]: The number of characters you want to extract.
Example
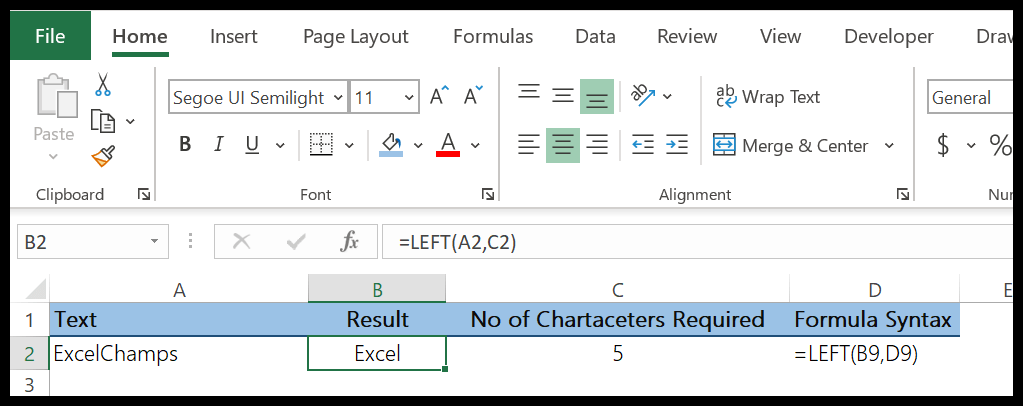
In the below example, we have extracted the first five digits from a text string using LEFT by specifying the number of characters to extract.
In the below example, we have used LEN and FIND along with the LEFT to create a formula that extracts the name from the cell.
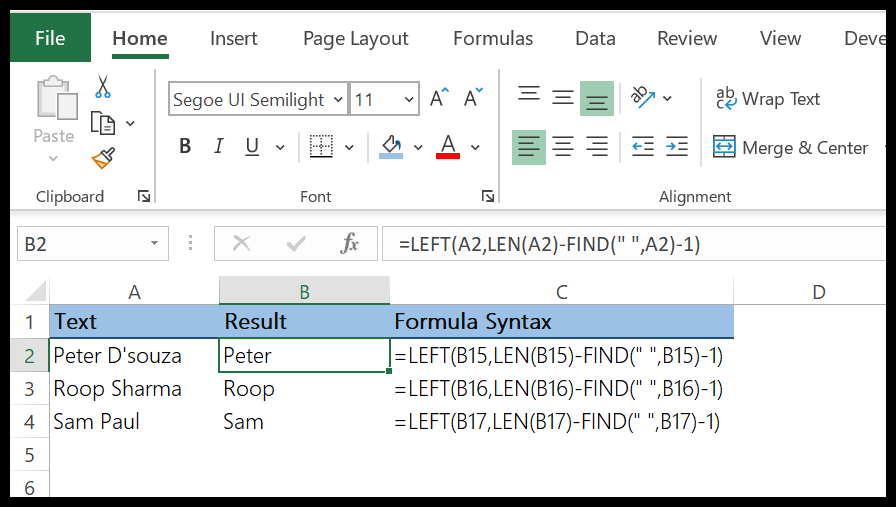
5. RIGHT Function
The RIGHT function returns sequential characters from a string starting from the right side (ending). In simple words, with the RIGHT function, you can extract characters from a string from its left side.
Syntax
RIGHT(text,num_chars)
Arguments
- text: A text or number from which you want to extract characters.
- [num_char]: A number of characters you want to extract.
Example
In the below example, we have extracted 6 characters using the right function. If you know, how many characters you need to extract from the string, you can simply extract them by using a number.
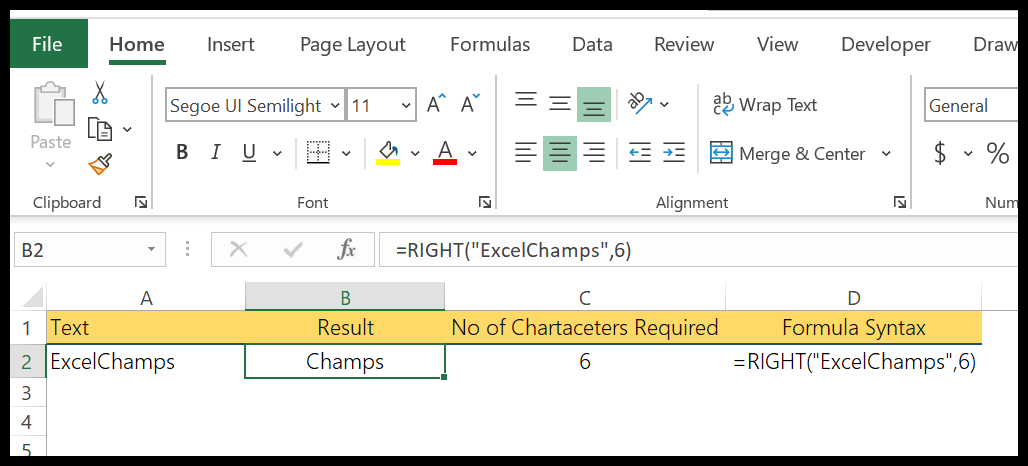
Now, if you look at the below example, where we have to extract the last name from the cell, but we are not confirmed about the number of characters in the last name.
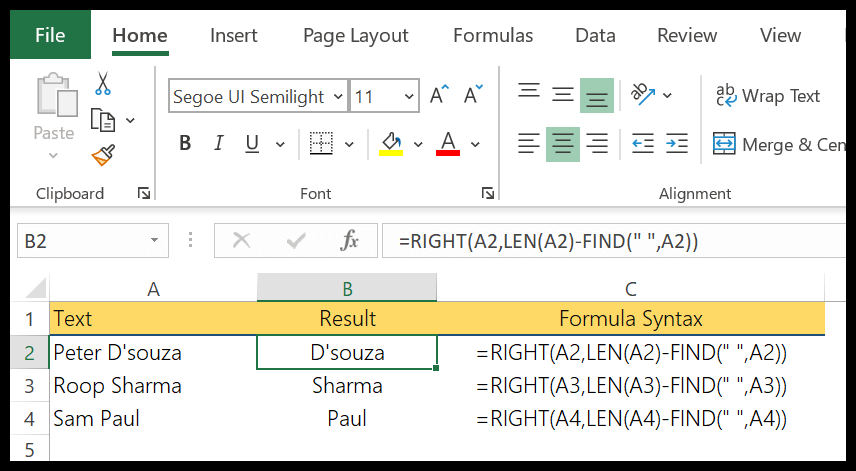
So, we are using LEN and FIND to get the name. Let me show you how we have done this.
First of all, we have used the LEN to get the length of that entire text string, then we used the FIND to get the position number of space between first and last names. And in the end, we have used both the figures to get the last name.
Arguments
- value1: A cell reference, an array, or a number that is directly entered into the function.
- [value2]: A cell reference, an array, or a number that is directly entered into the function.
6. MID Function
MID returns a substring from a string using a specific position and number of characters. In simple words, with MID, you can extract a substring from a string by specifying the starting character and number of characters you want to extract.
Syntax
MID(text,start_num,num_chars)
Arguments
- text: A text or a number from which you want to extract characters.
- start_char: A number for the position of the character from where you want to extract characters.
- num_chars: The number of characters you want to extract from the start_char.
Example
In the below example, we have used different values:
- From the 6th character to the next 6 characters.
- From the 6th character to the next 10 characters.
- We have used starting a character in negative and it has returned an error.
- By using 0 for the number of characters to extract and it has returned a blank.
- With a negative number for the number of characters to extract and it has returned an error.
- The starting number is zero and it has returned an error.
- Text string directly into the function.
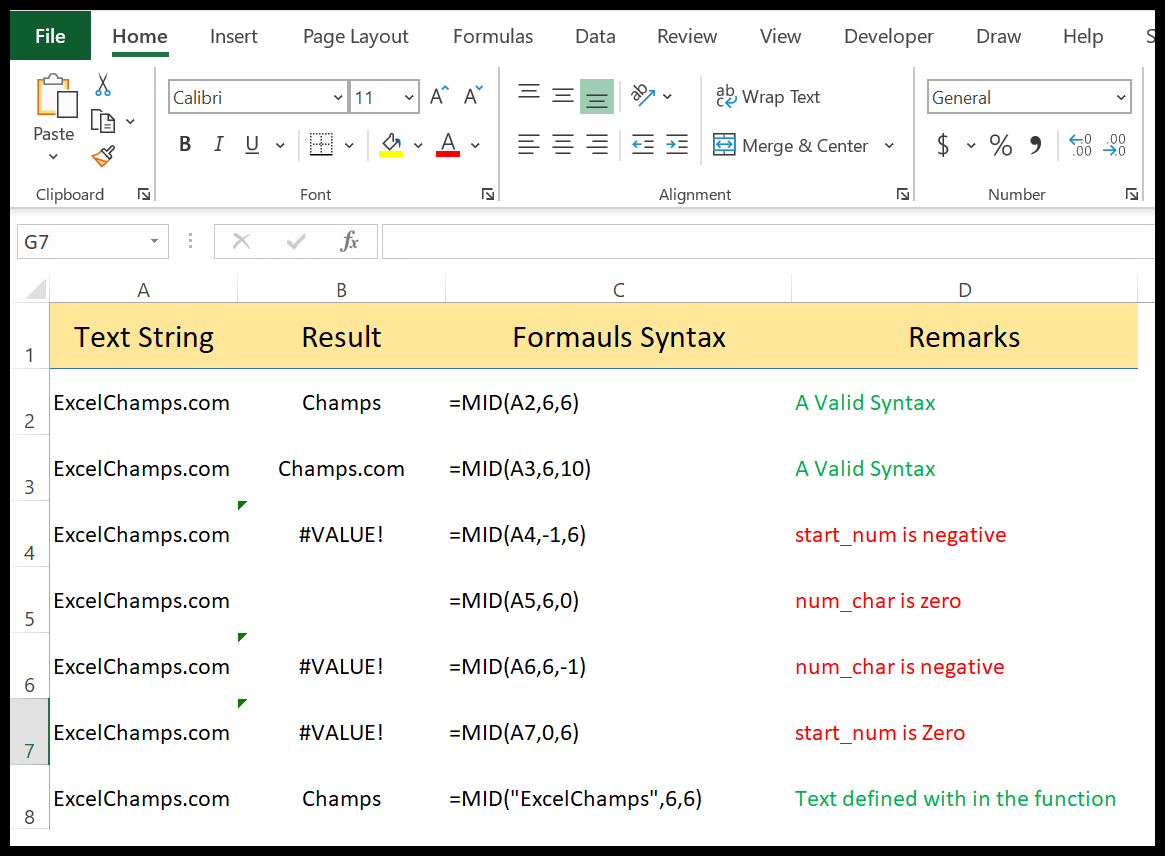
7. LOWER Function
LOWER returns the string after converting all the letters in small. In simple words, it converts a text string where all the letters you have are in small letters, numbers will stay intact.
Syntax
LOWER(text)
Arguments
- text: The text which you want to convert to the lowercase.
Example
In the below example, we have compared the lower case, upper case, proper case, and sentence case with each other.
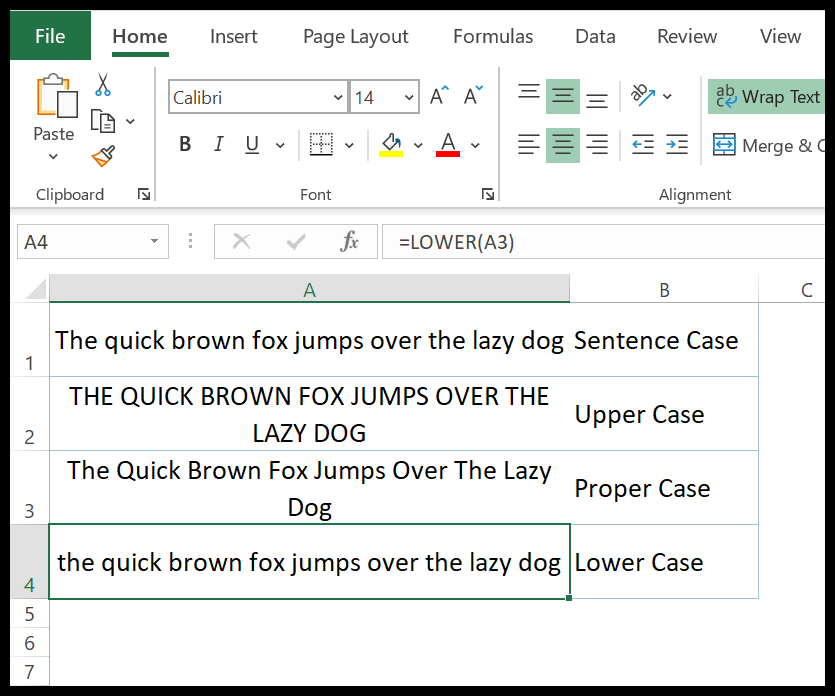
A lower case text has all the letters in a small case compared to others.
8. PROPER Function
The PROPER function returns the text string into a proper case. In simple words, with a PROPER function where the first letter of the word is in capital and rest in small (proper case).
Syntax
PROPER(text)
Arguments
- text: The text which you want to convert to the proper case.
Example
In the below example, we have a proper case that has the first letter in the capital case in a word and the rest of the letters are in the lower case compared to the other two cases lowercase and uppercase.
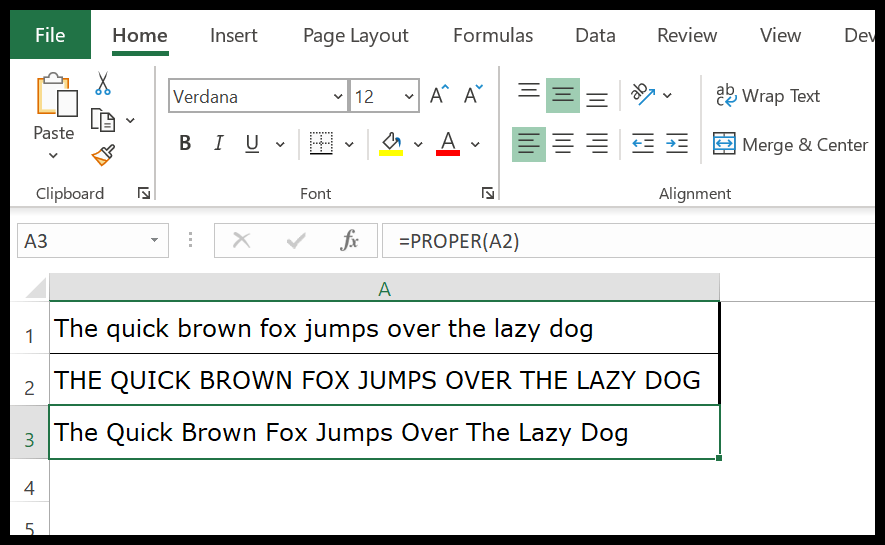
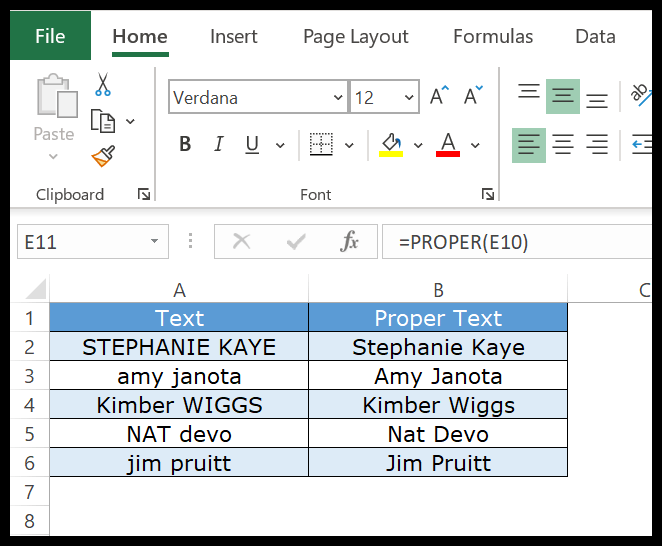
In the below example, we have used the PROPER function to streamline first name and last name into the proper case.
9. UPPER Function
The UPPER function returns the string after converting all the letters in the capital. In simple words, it converts a text string where all the letters you have are in capital form and numbers will stay intact.
Syntax
UPPER(text)
Arguments
- text: The text which you want to convert into uppercase.
Example
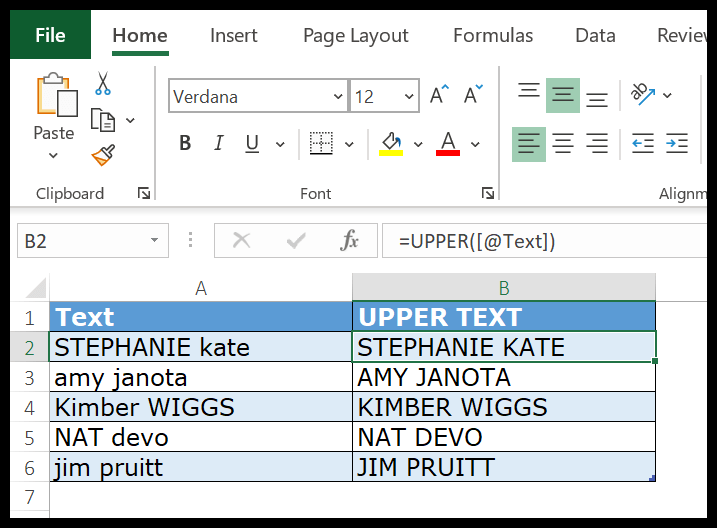
In the below example, we have used the UPPER to convert name text to capital letters from the text in which characters are in different cases.
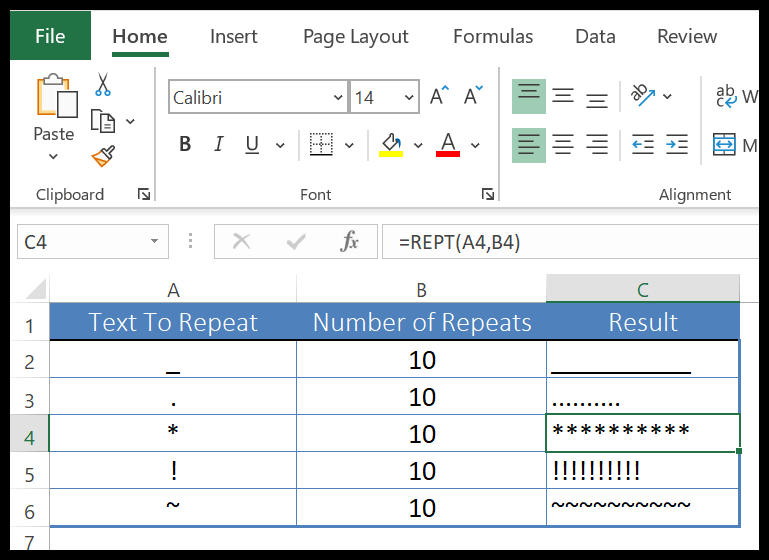
10. REPT Function
REPT function returns a text value several times. In simple words, with the REPT function, you can specify a text, and a number to repeat that text.
Syntax
REPT(value1, [value2], …)
Example
In the below example, we have used different type of text for repetition using REPT. It can repeat any type of text or numbers and even symbols that you specify in function and the main use of the REPT function is for creating in-cell charts.
Hi
Is possible to sum all WA11?
(A1) WA11 4
(A2) AdBlue 1, WA11 223
(A3) AdBlue 3, WA11 32, shift 4
… and everything is in one column.
Thanks you very much for your help.
Sincerely Marko
Your example formula in section 4 regarding returning the first name doesn’t work appropriately if you use a name like “Peter Jay”. It’s only working appropriately because the last name of each example is exactly one character longer than the first name. If you use =LEFT(B2,FIND(” “,B2)-1) that will return the first name regardless of the length of the first name or last name.